Curabiom® flora
For the maintenance of the intestinal mucosa1
All-round and innovative „fuel“ for diverse intestinal bacteria
With the water-soluble dietary fibre: acacia fibre, inulin, GOS, XOS and 2’FL

Package size: 14 sachets (16.2 g per each)
Gluten-free and no dyes.
Curabiom® flora combines the innovative water-soluble dietary fibres acacia fibre, inulin, GOS, XOS and 2'FL with vitamin B12 and biotin from natural sources. It thus, provides a comprehensive nutritional offer for the different intestinal bacteria in the various intestinal sections. At the same time, the powder preparation can be used for the intestinal mucosa care and the contained vitamin B12 has a function in cell division.
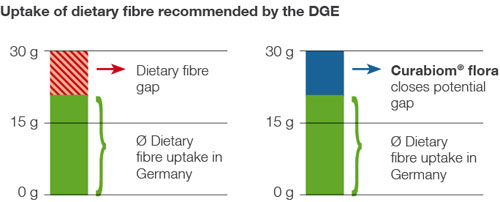
Why is dietary fibre so important?
Dietary fibres are particularly relevant for the intestines and serve as "food" for the intestinal bacteria. The fibres, which come from plants, are mainly found in fruit, vegetables and wholemeal products. According to the recommendation of the German Nutrition Society (DGE), adults should consume at least 30 g of dietary fibre per day. However, current studies show that the average dietary fibre intake in Germany is far below the recommended 30 g.

Package size: 14 sachets (16.2 g per each)
Gluten-free and no dyes.
The importance of the intestinal mucosa
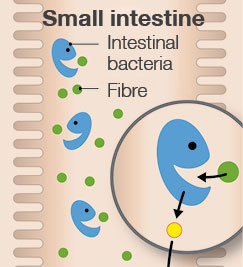
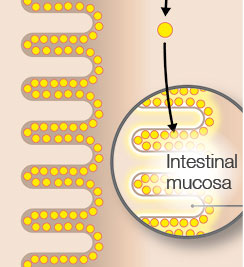
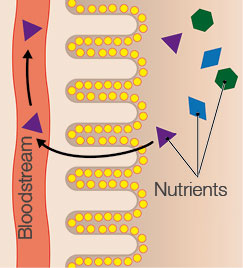
The intestinal mucosa serves as a natural barrier to the outside world, and as a kind of “firewall”, ensures that only essential substances reach the intestine. It, conversely, locks out unwanted substances. It interacts with the intestinal bacteria, which form the intestinal flora, and helps to transport nutrients to the bloodstream.
In order to be able to fulfil its key function in the long-term as well, the intestinal mucosa regenerates every three to six days. It can therefore, be counted among the body’s fast dividing tissues. Some 200 g of intestinal cells are broken down and replaced by new ones each day. This takes a great deal of energy. The intestinal mucosa gets some 60 to 70 percent of this energy from short-chain fatty acids, which are formed from the intestinal bacteria’s fermentation of dietary fibre.
Fermentation of dietary fibre in the intestine
The bacteria living in the intestine ferment the dietary fibre. This produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFA). They play an important role in the functioning of the intestinal mucosa.
What dietary fibres does Curabiom® flora contain?
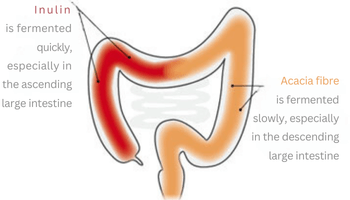
Acacia fibre
It originates from the so-called exudate (latex) of the acacia tree, which is mainly native to the Sahel region of Africa. The acacia fibre contains over 80 percent of soluble dietary fibre. It is fermented slowly in the large intestine, has a low glycaemic index and is low in calories.
Inulin
Inulin is a natural and tolerated fibre obtained from chicory. It is fermented more quickly in the ascending large intestine and serves as food especially for bifidobacteria and lactobacilli.
GOS
The short-chain galacto-oligosaccharides are very similar to the milk oligosaccharides, which are to be found in breast milk. For humans they are more readily usable than long-chain plant-based substances (e.g. fructo-oligosaccharides).
2'FL
2’-O-Fucosyllactose (2’FL) is sofar the most intensively researched milk oligosaccharide (HMO). The complex carbohydrate is found naturally in breast milk and is the main distinguishing factor from cow’s milk.
XOS
The xylo-oligosaccharides are particularly innovative. This dietary fibre is obtained from fermentation and has been documented as having a positive effect in numerous studies.
Curabiom® flora duo Darmkur1
Fiber & 22 bacterial strains
For those who want to supply their intestines not only with dietary fibre but also with lactic acid bacteria, we recommend the Curabiom® flora duo Darmkur. In addition to the innovative water-soluble dietary fibres from Curabiom® flora, this combination preparation also contains 22 high-quality and specially selected lactic acid bacteria strains in a very high dosage of 60 billion per day. The preparation thus provides living bacteria and their "food" in one. Due to the vitamins it contains, the duo preparation supports the mucous membranes, cell division and the immune system and can be ideally used as an intestinal cure, e.g. after antibiotic therapy.
The SCFA formula by Dr. Wolz
SCFA translates as short-chain fatty acids, which are produced by the fermentation of intestinal bacteria. The water-soluble dietary fibres are particularly relevant, as they can be well utilised in the intestine. In Curabiom® flora or Curabiom® flora duo Darmkur these dietary fibres are present in a unique formulation - the SCFA formula. It ensures a comprehensive supply of different types of bacteria and is thus also an energy supplier for the intestinal mucosa. The formula of acacia fibre, inulin, XOS, GOS and 2'FL was developed exclusively by Dr. Wolz for the two new multi-fibre preparations Curabiom® flora and Curabiom® flora duo Darmkur.

Package size: 20 sachets an 40 capsules
Gluten-free and no dyes.
22 different probiotics:
- Bifidobacterium bifidum Bb-02
- Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus Lb-87
- Bifidobacterium Breve M-16V
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG
- Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM
- Bifidobacterium lactis HN019
- Bifidobacterium longum BB536
- Bifidobacterium infantis M-63
- Streptococcus thermophilus St-21,
- Bifidobacterium breve Bb-18
- Lactobacillus gasseri Lg-36
- Lactobacillus plantarum Lp-115
- Lactobacillus casei Lc-11
- Lactobacillus reuteri 1E1
- Lactobacillus acidophilus La-14
- Lactococcus lactis Ll-23
- Bifidobacterium lactis Bl-04
- Lactobacillus brevis Lbr-35
- Lactobacillus paracasei Lpc-37
- Lactobacillus salivarius Ls-33
- Lacto bacillus fermentum SBS-1
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus Lr-32
1 Biotin contributes to preserving the normal mucosa (e.g. the intestinal
mucosa).
2 Vitamin B12 has a function in cell division.
3 Vitamin B12 contributes to the normal function of the immune system